Meta Description: Learn the differences between die casting vs investment casting manufacturing process, as well as sand casting . Read the differences in costs, production volumes, materials, tolerances, applications to select the correct approach to use in your project.
The current manufacturing needs precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in casting processes of metals, especially during high volume production runs for medium sized parts . Die casting and investment casting are two prevailing techniques that can be singled out in industrial production, and they both possess some unique benefits that are suitable to this or that application of the casting method. . Knowing the underlying contrasts between these two processes will be very important to manufacturers, engineers and entrepreneurial owners who require the best of solutions to his or her needs of metal components.
Both die casting and investment casting are quite different methods of producing metal components and each has its strong points compared to the other, especially when it comes to intricate parts that require different approaches to achieve fine detail . , so it is necessary that they each be utilized in the most appropriate production situations. Investment casting entails injecting wax to an aluminum cavity. Alternatively, the die casting involves high pressure that pushes molten metal into the mold cavity of the dies. The difference is basic and this will influence the whole course of their use; about the selection of materials to their final product features.
Companies, which deal with global manufacturing and logistics such as Shenzhen Guanwutong International Freight Forwarding Co., Ltd. (GWT Worldwide), need to know these manufacturing processes related to metal casting, including ferrous metals . . GWT worldwide is one of the professional logistic companies that deal in the aspect of global freight forwarding and supply chain solutions where its role entails helping businesses solve the setup of the global freight forwarding and flow chains as well as facilitating global transportation of the cast portion of the production plants to their markets worldwide through their wide scaled air/ sea freight and custom clearance services.
Understanding Die Casting Process Fundamentals
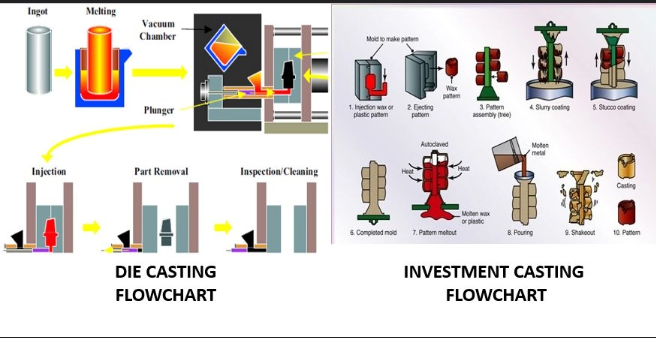
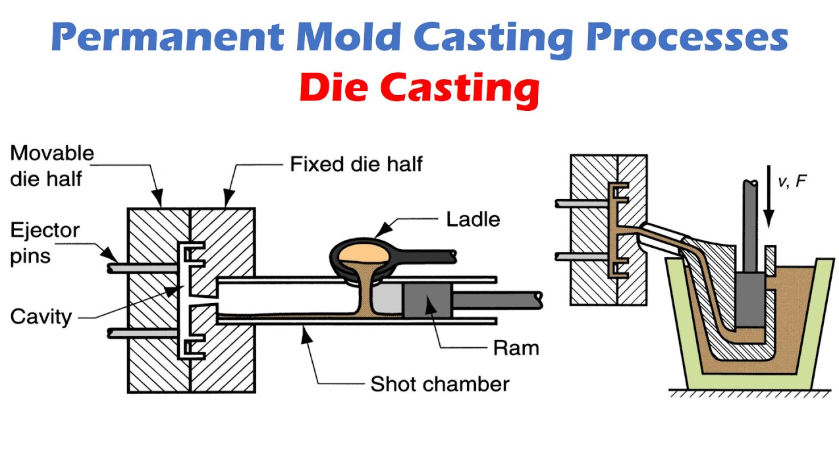
Die casting is one of the most effective production methods of manufacturing mass quantity metal parts, including those with thin walls for specific applications. , including thin walled parts that are made from non ferrous metals,with enormously high uniformity. This is a process that involves this permanent steel molds or what is commonly referred to as dies which are precision machined to produce specific specifications regarding each and every component. These dies are then filled with molten metal at a very large pressure, usually 1 500 to 25 000 pounds per square inch.
High-pressure injection guarantees a full filling of the mould and yields parts of high surface finish and dimension precision. The difference between die casting and investment casting is that it can utilize a permanent mold or die, which does not have to be re-made on every casting cycle. This benefit of permanent mold is what makes die cast parts especially cost effective, reducing the need for extensive post processing . at large volume production runs where the tooling outlay can be offset over thousands or millions of castings.
The procedure starts by melting the metal until it reaches the optimum pouring temperature and then injected into the die cavity at high speeds to form a solid block . Solidifications occur under high pressures, thereby guaranteeing dense, and plagueless casting with tight tolerances . After solidification, the die is opened and the finished part is expelled to any secondary operations that are required.
Investment Casting Process Deep Dive
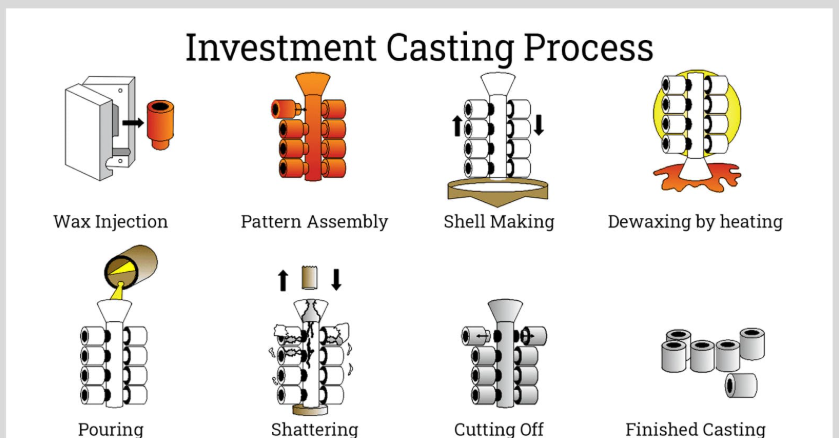
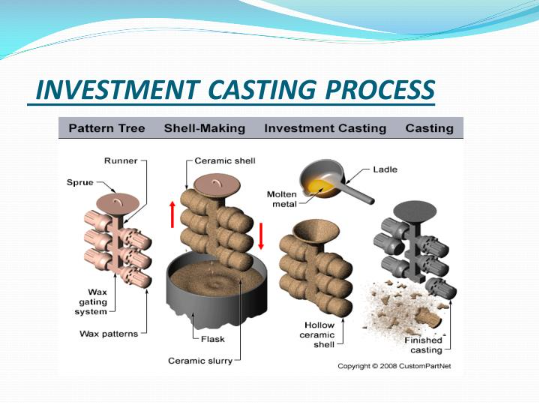
Lost wax casting, which is also referred to as investment casting is one of the oldest and most accurate metal forming processes currently in common application in modern manufacturing, especially in discussions about casting vs die casting methods . In this process, lost wax casting creates highly detailed components that are produced in a several-stage process that starts with making a wax pattern (in the exact shape of the investment cast parts represented by the desired part.) after which molten metal is poured into the pattern to produce the final part.
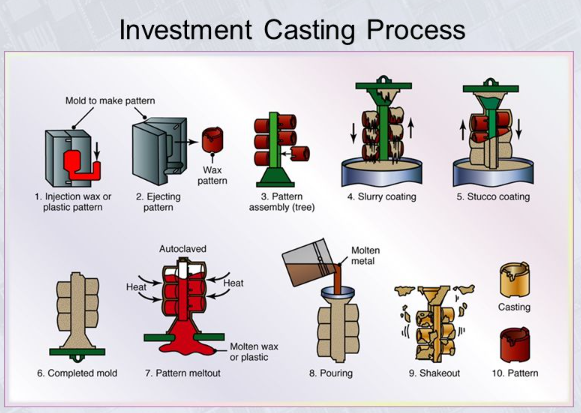
The wax pattern is placed on runners and gates, and the end is then sprayed with successive coats of ceramic slurry to make a firm shell mold. The ceramic shell is then hardened and a heating process follows which melts out the wax leaving a hollow cavity inside the ceramic mold, similar to processes found in hot chamber systems . The process has a principle central to its alternate definition, the lost-wax process which enables complex internal passages and complicated geometries that require high dimensional accuracy, unlike other casting processes . that would not be possible by other structural castings.
The molten metal is then urgently poured in the ceramic mold, usually under gravitational power or low pressure. The ceramic shell is chiseled off upon the cooling to expose the finally complete casting of the desired part. . It is well suited in creating components, whose surface finish is excellent, complex internal work and tight dimensional tolerances often discussed in die cast vs investment cast comparison .
Material Compatibility and Selection
Choice of material is another crucial difference between die casting and investment casting procedure. The parts cast via the die casting process are mostly the non-ferrous metals that melt at a lower temperature, often utilizing a hydraulic system to achieve the necessary press . Therefore die casting is efficient using zinc, Aluminium, magnesium and brass. This is because of high pressures and fast cooling rates of the die casting process, which provides corrosion resistance, due to which ferrous materials might experience thermal shock.
Investment casting has much greater material compatibility, and both ferrous and non-ferrous alloys are accommodated. Die casting can only be applied on non ferrous metal casting whereas investment casting can apply ferrous or non ferrous metal, utilizing a refractory mould for better heat retention . This flexibility has caused investment casting to be the choice of casting method when stainless steels, tool steels, superalloys and other high performance materials, including refractory material, are needed.
The die casting material limitations are compensated with high performance on the use of aluminum, zinc and magnesium alloys, making it a favorable casting method . These high pressure flow well, solidify quickly, and when die cast create parts from molten material with achieving a net shape with superior mechanical properties and surface finish while maintaining tight tolerances ..
Production Volume Considerations
The requirements of production volumes play a major role in the selection between die casting and production volume investment casting. DC is the most suitable when faced with a large production run and/or high-volume project due to the fact that DC produces superior consistency and repeatability compared to sand casting, making it efficient to produce parts in large quantities. Die tooling is a highly costly investment which is economically viable to pursue given high quantities of production alone.
Die casting is optimal in high volume applications when it is necessary to have several thousands or millions of the same product, which is typical in high volume production runs . The solid tooling offers outstanding repeatability, whereby any part-to-part variation is at the minimum due to the high pressure, controllable process. Cycle times are usually expressed in terms of 2nds to minutes and hence cold chamber die casting works extremely well when it comes to mass production compared to other casting methods. .
Investment casting is applicable to a variety of volume needs, including production volume investment casting as it is cost-effective to low-volume and medium production. Ingots or parts costs individually might be expensive than die casting when produced in large volumes, but we should all agree that the flexibility of setup and reduced material cost of tooling makes investment casting quite appealing in special applications, prototyping, and medium production lengths.
Dimensional Accuracy and Tolerances
The two processes simulate outstanding dimensional accuracy, albeit by various means. Die casting and investment casting each have the ability to provide close tolerance dimensions and they are both excellent on small precision products. The accuracy that is obtained by each process is as a result of their characteristic of process and tooling strategies, particularly evident when the metal solidifies .
The accuracy of the steel dies that are machined precisely and high-pressure metal injection are obtained with die casting. Most common tolerances are either +- 0.1mm to +- 0.3mm depending on part size and complexity. The permanent tooling provides a repetitive set of dimensions on large production run with minimal variation of the parts.
The wax pattern and ceramic shell molding process results in similar or higher dimensional precision of investment casting as the metal solidifies . Tolerances of 0.13mm are normally obtained and even tighter tolerances can be obtained on crucial dimensions. The process does very well in terms of accuracy in complex shapes and interior details that could be problematic to other casting processes.
Surface Finish Quality Comparison
Quality of surface finish is another aspect in which both the processes are high and the superior finish is reached through different mechanisms. Die casting gives good surface finishes, which are usually direct casting, and need little in the way of post-processing. Fine surface textures of parts can be achieved by the smooth surfaces of the steel dies along with high pressures of metal injection without any further finishing on the parts making them adaptable in numerous applications compared to other casting methods .
Investment casting has the advantage of titanium producing near-perfect surface finishes with the fine ceramic shell. The ceramic surface is smooth and is transferred to the casted part and it produces finishes that can competes well with machined surfaces. Numerous investment cast components do not need any final surface treatment, and they can be assembled or put in use immediately, ensuring quality in each cast part .
The selection of a process usually depends on the particular surface needs and after treatment capabilities, particularly in the context of casting vs different method . The two processes are capable of high-quality finishes that can be used in a high-end application, although investment casting might slightly outweigh the surface finishing needs of parts demanding the highest quality.
Complex Geometry Capabilities
The main difference between these processes is the capability of geometric complexity. When the product that needs to be casted is complicated in design or consists of complex components, then die casting method is preferable. In investment casting, because the complex areas in the cavity are difficult to be filled by the liquid metal. This evaluation must however take into detailed consideration the nature of complexity in question.
Die casting is better in hard to make complex external shapes and features which can be a part of the permanent die tooling. The deep feed injection makes certain that intricate die details are totally filled leaving sharp edges, small details, and complicated exterior design. Die casting however can also not be used to make internal passages or undercuts that will allow ejection of the parts within the permanent dies.
The investment cast manifested better lastability of internal intricacy, hollow structures and complex internal channels. Having them actually machined out of metal takes intricate internal geometries which is impossible using permanent tooling. This makes investment casting suitable to the manufacture of parts such as turbine blades, pumps impellers and other parts with internal cooling passages or internal complex shapes and components.
Cost Analysis and Economic Factors
Cost factors include the initial tooling investments as well as the part costs. Die cast technologies involve large upfront cost to manufacture precision steel dies that may cost to tens of thousands of dollars to hundreds of thousands of dollars based on the part complexity and size. The die casting is however quite expensive in low volume production hence suitable in large production volumes due to the inherently low costs of die casting.
Investment casting engages lower start-up tooling fitting, with the major expenditure on wax pattern tooling and production fitting. Investment casting has a flexible and slightly lower setup cost compared to the sand casting method. due to the expendable character of the ceramic molds, which implies continuing material costs per casting cycle, but it is cost-efficient in lower volume production and in development of prototypes.
Economics should be done on the basis of the complete cost of the program including tooling, per-part costs, secondary operations, and quality aspect. In high volume casting, the thumps go to die casting but in the low to medium volumes and with special applications investment casting is cost efficient.
Lead Time and Production Speed
The process selection decision frequently depends upon the speed of production and lead time requirements. Die casting saves a lot of time compared to investment casting and is suitable to use when there is high production alongside packing sand. , especially in cold chamber die casting . Die casting has fast cycle times and permanent tooling that makes it a good method because of its fast turnaround when it starts production.
Die casting takes between 30 seconds to several minutes (depending on part size and complexity), that is why die casting cycle time is longer than injection molding. After the dies are created and production lines are ready, the molds are used to produce parts continuously with the minimum manufacturing off days.
Investment casting takes up more time because of multiple processes in which a wax pattern is created, shell is constructed, dewaxed, casted, and shell is removed. Nonetheless, cluster assemblies can process several components at once, which facilitates achieving a better overall throughput at appropriate applications.
Size and Weight Limitations
The size and weight handling capabilities vary a lot in these processes. IC has the capacity to take parts weighing as little as an ounce to around 200 pounds. Investment casting is highly flexible in accommodating a wide variety of very small precision pieces as well as larger structural castings, as is constrained more by the equipment available within the foundry.
Die casting is perhaps best suited to dealing with small to medium sized components and die construction, clamping power and metal injection systems set practical limits. Die castings produced on a very large scale are asking a lot of investments in terms of equipment and tooling, which are not even economically viable.
Even the weight distribution also contributes to the final process selection, with investment casting proving more suitable to the part that has a large weight variation within a single casting whereas die casting is perceived to do well with the uniform thickness of walls and weight balance.
Quality Control and Repeatability
An important aspect of the selection of manufacturing processes is quality control and repeatability. The second strength of die casting is its repeatability, which is outstanding because the tooling is permanent and the variables of the process strictly maintained. Die casted parts have superb consistency and repeatability, and this is why die casting is most suitable in application where a tight statistical process control is involved.
Die casting has permanent dies and automated process controls that reduce variation within parts, and thus achieving predictable quality. The methods of statistical process control are easily applicable to allow observation and adherence to the standards in terms of quality during the production runs.
The process control in the multi-step process is a more significant factor when it comes to the investment casting quality. Although able to create high quality parts, the use of refractory material in the process makes them challenging to make with consistency requiring much care be taken with the wax pattern in terms of quality, the parameters of the shell building and the pouring method.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Manufacturing process selection is ever more dependent on environmental issues and aspects of sustainability. In large volume production, less wastage is involved per piece over time due to the permanence of the tooling involved in die casting, so that the die can handle hundreds of thousands of pieces before needing re-tooling. The fast production cycles lead to the energy efficiency in high-volume cases, as well.
Each part of investment casting produces more waste because of expendable ceramic shells and wax patterns. Nevertheless, investment castings processes in metal casting follow recycling activity of ceramic materials as well as reclamation of wax materials to reduce environmental interventions.
The metal recycling is advantageous to both processes with scrap and runners usually melted and reused in future casting procedures. Environmental impact of all the processes should be taken into account especially the lifetime impact of process on the environment, such as tooling manufactured, amount of energy or waste produced.
Industry Applications and Use Cases
The supplementary characteristic of these casting processes is elicited through the industry applications. Die casting is common in making automotive parts, housings of consumer electronics, parts of appliances and other systems that need a large number of similar non ferrous metals parts on a regular basis. The auto industry stands to be one of the major beneficiaries of the lightweight superior strength to weight ratio provided by die casting using aluminum.
Investment casting is used in the aerospace industry, medical device industry, jewelry industry and industrial equipment industry where the more emphasis is placed on precision, variety of materials used and geometrical complexities than volume production. Investment casting is commonly used to complete aerospace turbine blades, medical implants and industrial parts where the product yield of dealing with exotics and unusual shapes is paramount.
The two processes are applicable in a number of industries and both are selected based on a given industry project and not necessarily basing on the industry one practices in.
Technology Advances and Future Trends
Both casting processes are getting more and more polished through technological innovation. The die casting is favored with better die materials, enhanced process monitoring, automation systems and technologies making it more efficient and superior. Other new die casting technologies are vacuum-assisted die casting and semi-solid processing to supplement die casting processing.
Advancements in investment casting have been to the area of shell system, refractory material automation of the wax pattern and more sophisticated simulation tools dealing with casting layout design.
The two processes are still undergoing changes to satisfy the growing requirements of precision, efficiency, and sustainability in the industrial world today.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
The decision to use die casting or investment casting must take into account many aspects, such as level of production, materials, geometrical complexity, quality, and economy. The moderate complexity of non-ferrous components, in high volume production, tends to be cast using die casting, ensuring the desired shape is achieved effectively. however, low-medium volumes or complex geometries or high requirements of particular materials are more apt to receive investment casting.
It is important that in coming up with the decision that such advice can be sought by considering the opinion of members of the casting community that would have had experience in areas of specific needs and advise in which way would be the most suitable way. A hybrid approach, whereby investment casting is used in development of a prototype and low volume-casting production with transition to high volume die casting solution, can be beneficial to many projects.
Firms such as GWT Worldwide are very relevant in the international supply chain of casting where they offer imperative logistic services such as air freight services, sea freight services, China to Europe railway services and customs clearance services to enable the components of the cast attain their destinations in an efficient and cost effective manner.
Conclusion
The advantages of die casting and investment casting as metal casting processes re different and will be appropriate to use under varied manufacturing situations. The die casting process has an advantage of having high production volumes and the non-ferrous parts have very good consistency together along with the advantage of quick production cycles whereas the investment casting process is more flexible with regards to geometric complexity, wide material range use, and precision requirements. The selection of one of these processes over the other should not rely on a generalized approach; it should be made, by analyzing production demands, quality and economic reasons.

