Introduction
Casting is among the oldest and most diverse industrial techniques made by mankind. Over 7,000 years old, it is one of the most fundamental ways of production, used in a wide variety of industries, including aerospace and jewelry-making metal casting process. The process is carried out by pouring or injecting hot material into a mold that allows the material to solidify and cool and then the new part is extracted. Its long-lasting fame is explained by capabilities to provide high flexibility in manufacturing multi-material, high strength, and made-to-shape components at different production levels.
1. What is Casting?
One of the manufacturing processes is called casting; in this process molten material is poured/poured into a pre-designed mold and then cooled and solidified in a given shape liquid metal. It is applied in different industries owing to its capacity to generate complex geometries and components which could otherwise be very costly or challenging to fabricate using alternative methods casting metal.
2. How Casting Works
The casting process usually entails the formation of mold (shaped to resemble the desired part), melting of the selected material to a molten state and pouring or injecting the molten material into the mold cavity wax pattern. The part is then cast in liquid form, after cooling and solidification it is cast out and completed usually by means of machining, grinding or surface finishes.
3. Essential Components of Casting

Such important aspects in casting process entail:
- Pattern or Master Pattern: This is the first model that defines the cavity.
- Mold: The receptacle in which this molten material lies.
- Gates, Sprues and Vents: Openings to allow materials to enter the mold and air to get out.
- Flash: unneeded material that can be reduced once solidified.
- Net Shape: It is the final shape with minimum post-processing.
4. Popular Materials Used in Casting

Such materials are common:
- Metals: lead, copper, zinc, aluminium, iron.
- Alloys: Brass, bronze.
- Porcelain, Clay.
- Rubber and plastics.
- Composite Materials: Fibers and Resins.
- Concrete and Glass.
5. Sand Casting
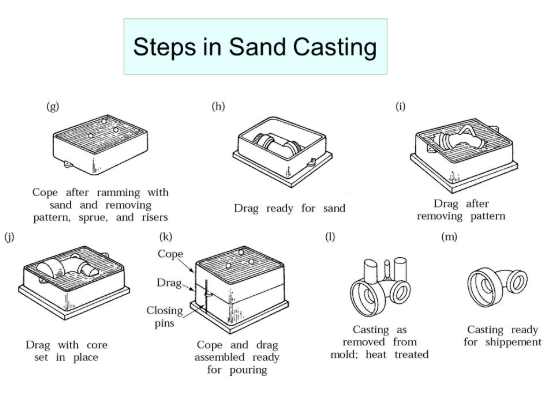
This antique process involves the formation of molds using silica sand. The mold is filled with molten metal and once set, the mold which is usually made of sand is broken casting materials. It is suitable to work with metals which have a high melting point such as steel and titanium smooth surface finish.
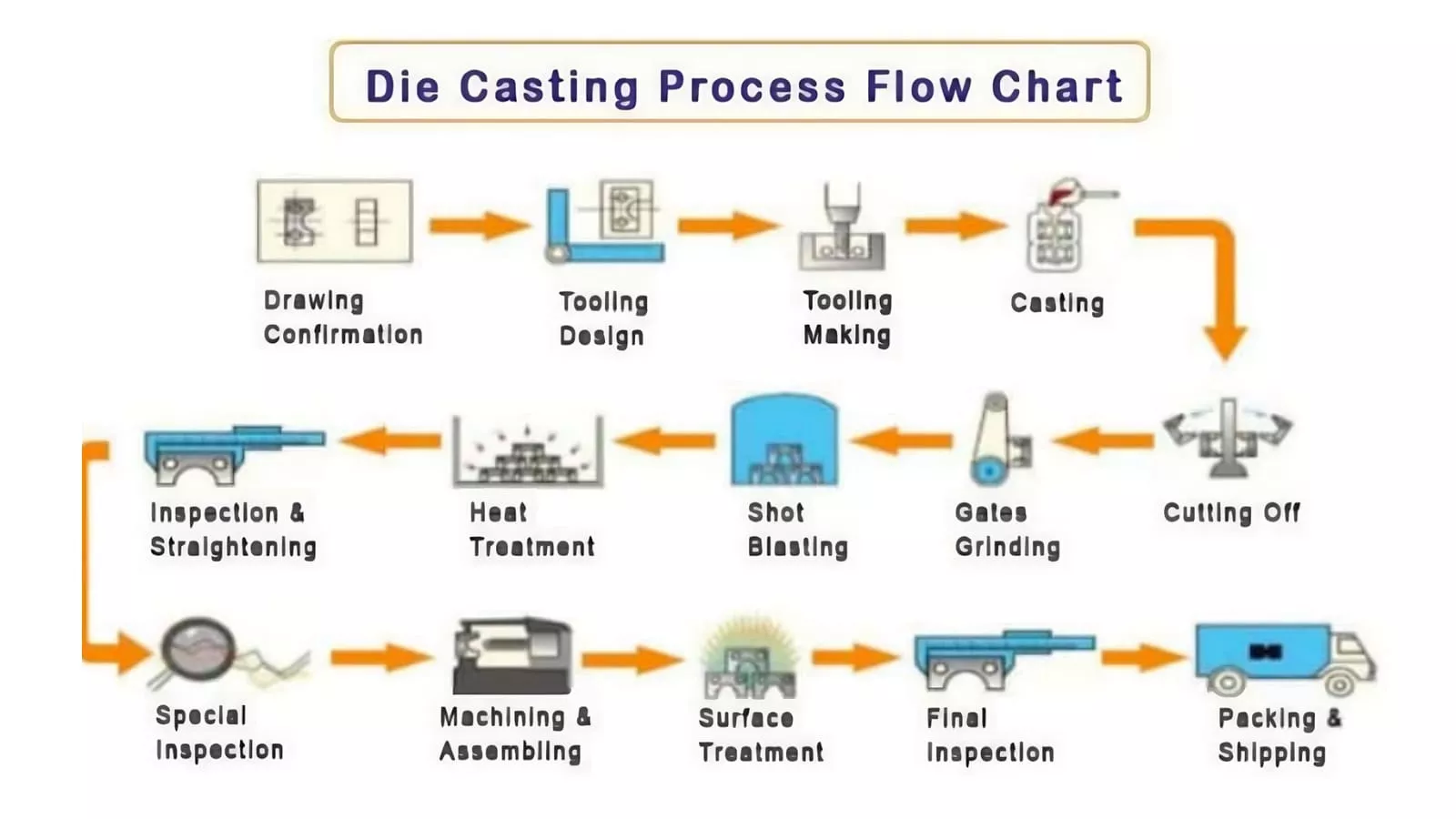
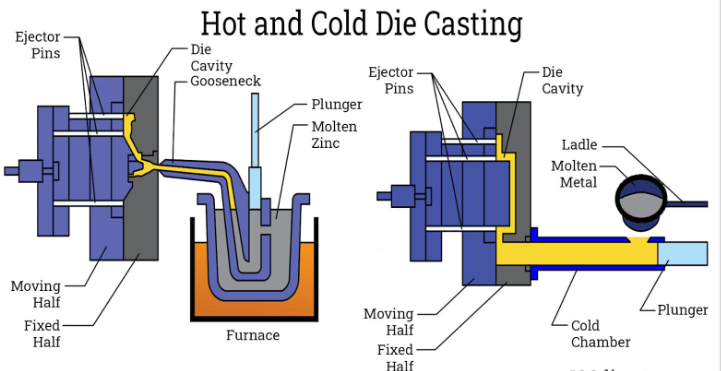
6. Die Casting
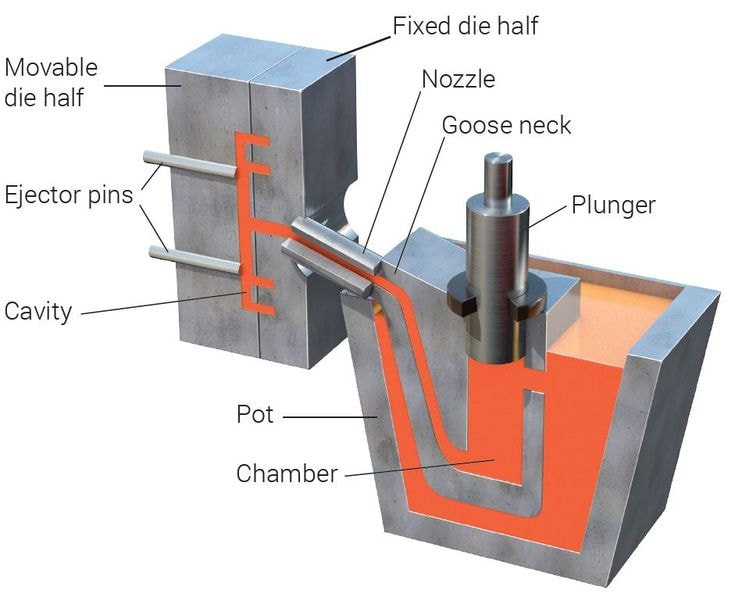
The DIE casting process involves permanent mold called steel molds and high-pressure injection of molten metal. It can be used on low melting point alloys like zinc and aluminum and it has a high degree of precision and repeatability ideal in mass production surface quality.
7. Investment Casting
The process is also referred to as lost-wax casting, where a wax casting is made, covered in a ceramic substance and the wax melted out lost foam casting process. The gap is filled with molten metal creating extremely precise complicated parts.
8. Gravity Die Casting
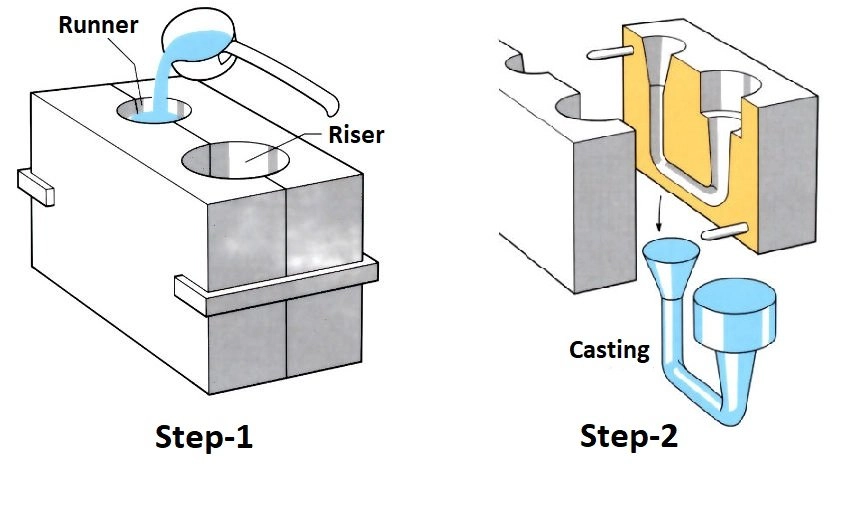
The gravity die casting simply deals with pouring molten metal into a metal mold under the forces of gravity. It is an economic method of fabricating well-finished mid-sized parts sand casting process.
9. Continuous Casting
Continuous casting is the main method: it was originally used with predominantly metals, but continuous casting is also used with other materials. The mechanics of continuous casting occur when something in the molten state can continuously flow into a mold with something in the solid state being removed. These are most suitable in the production of uniform billets, rods and tubes other casting processes.
10. Shell Molding
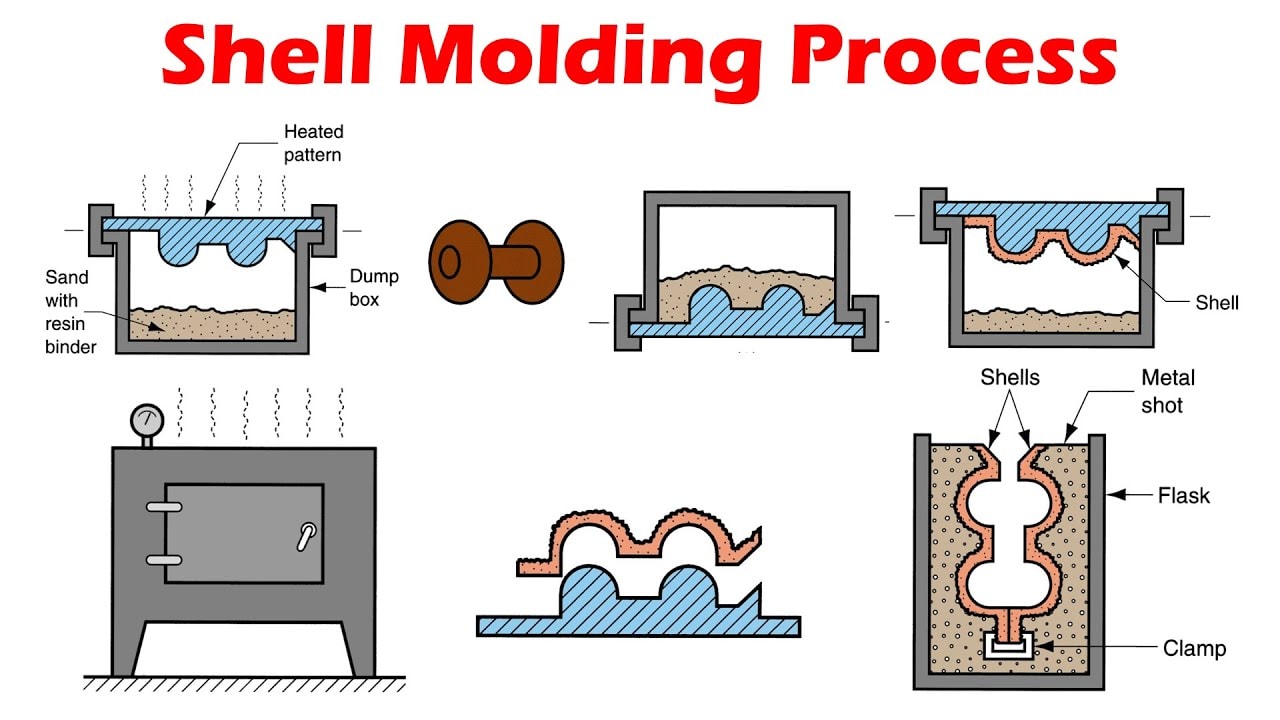
Shell molding is a variation of sand casting, which utilizes a heated pattern and a sand-resin Shell molding is a variation of sand casting, which utilizes a heated pattern and a sand-resin creating a very thin (high precision) shell. It can provide greater accuracy and more smooth surfaces than traditional sand molds ceramic shell.
11. Lost-Foam Casting
Lost-foam A foam pattern is coated with refractory material and sand-cast. The foam vaporizes when it comes in contact with molten metal, hence forming the part. It is applicable on complicated thin-wall items desired shape.
12. High-Pressure Die Casting
This is an injection process whereby molten metal is shot into hardened steel molds at high pressure. It makes components that have high detail finishes and have good mechanical characteristics and are usually seen in the automotive and electronics industries squeeze casting.
13. Centrifugal Casting process
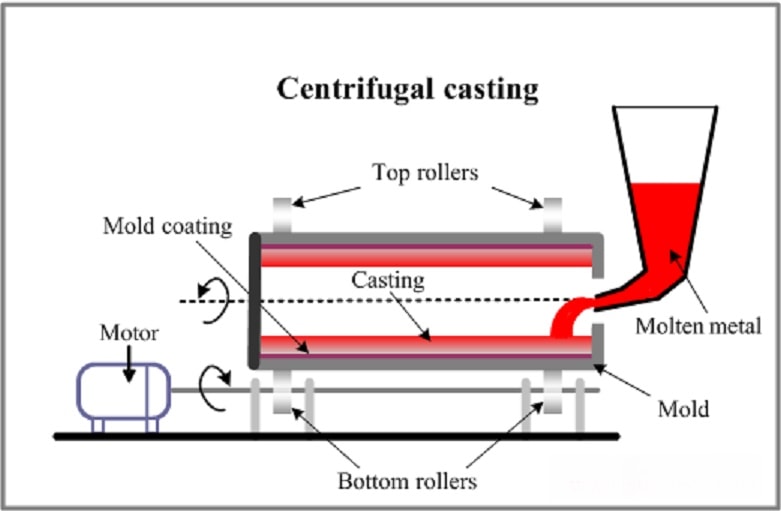
In this procedure the melted metal gets poured into a rotating mold create complex shape. The metal is centrifugally spread so it is ideal in cylindrical materials such as pipes and bushings.
14. Permanent Mold Casting
Permanent mold casting In a permanent mold casting process, metal molds can be reused cylinder heads. Melting is done and the liquid poured in to be solidified by gravity or pressure. It supplies decent dimensional precision and finish.
15. Vacuum Casting
Vacuum casting The mixture is poured into a mold and then drawn in under vacuum, minimising the amounts of air trapped and flaws in the piece aluminum alloys. Frequently applied in prototyping, and making low volumes of complex components.
16. Low-Pressure Casting
The mold cavity is filled with molten metal through low pressure. The result is high, defect-free dense parts with good dimensional repeatability.
17. Squeeze Die Casting
A combination of the die casting and forging processes, it involves pouring molten metal into a die and pressing on it to form dense poreless parts. Applied in cars and aircraft vacuum die casting.
18. Plaster Casting process
Like investment casting, plaster casting makes detailed parts by casting them in plaster of Paris molds. Suitable to mini production and small series, especially non-ferrous metals.
19. Modern Applications of Casting
Casting is used:
- Aerospace: Turbine housing, blades.
- Transportation: Engines, tires.
- Art and Sculpturing: Stats, ornaments.
- Medical: Surgical equipments, implants.
- Consumer goods: Kitchenware, toys.
20. Prototyping with Casting
Casting is a convenient solution to the prototyping process because it facilitates the creation of working, imperative complex pieces in light portions tricky and rapidly at a reduced cost liquid material. Such methods are especially commonplace as investment and vacuum casting.
21. Comparing Casting to CNC Machining
CNC machining involves taking material away, a solid block at a time as the shapes are molten, whereas in a casting process such shape is made out of material. Casting is sometimes favored when an object is complex or hollow and large scale production is involved whereas CNC machining is available with better precision on finer details traditional sand casting.
22. Questions to Determine the Right Casting Method
the choice of the correct casting technique is realized by answering the following question:
- What is it? What is the alloy?
- How much do you need in volumes?
- What does the size of a part look like?
- Is there a budget on tooling?
23. Innovations in Casting Technology
The most modern enhancements have been:
- 3D Printed: To make low volumes quickly.
- Automated Molding Lines: This will increase speed and consistency.
- Premium Alloys: Coming with high strength and corrosion resistant.
- Integrated Process Monitoring: To have a better quality control.
Conclusion
The application of casting in manufacturing has kept the manufacturing industry so long, and this is because of its flexibility and efficiency. Casting has been never surpassed in versatility or in economic advantages, whether in making the tools of early man, or the aerospace parts of an advanced civilization. However, the future of casting is clear with the incorporation of modern technologies and efficient logistics solutions that make it to be an undertaking that is not to be ignored in the meeting of various production needs.

