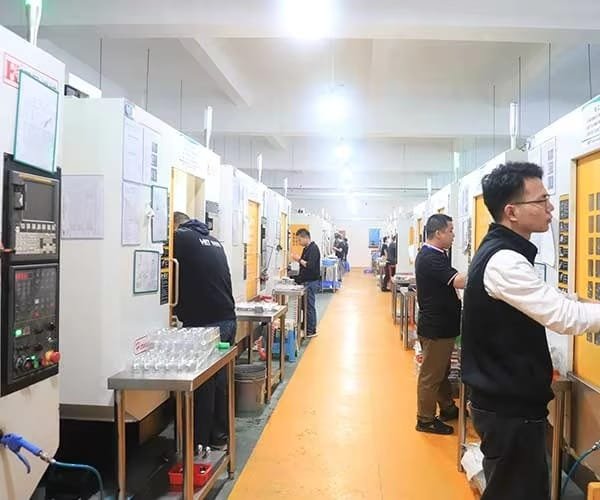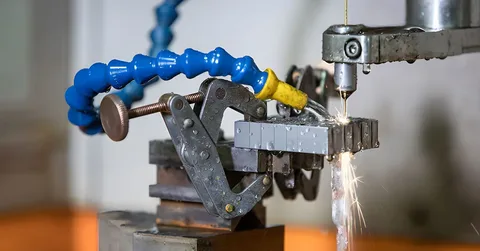
EDM wire cutting technology is one of the most important achievements so far in precision manufacturing, its accuracy and very high precision versatility in the cutting of metals is unobtainable in other manufacturing methods. A metal (often conductive) workpiece is cut or shaped by a wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) process which utilizes a very thin electrode wire typically a metal wire. The process has revolutionized the manufacturing of industries beyond aerospace to making little medical devices as the process allowed making complex components that would not be possible to make through the usual machining process.
Understanding the Fundamentals of EDM Cut Wire

The electrical discharge machining process has its roots somewhere in the 18 th century when Joseph Priestley noted that electrical discharges were able to remove materials off electrodes. But it is also important to note that the modern EDM cut wire technology we all recognize was first developed in the 40s during the discovery of Soviet researchers whose efforts actually brought about the beginning of the modern systems of wire cutting using EDM process. The mechanism of wire-cut EDM process is simple. Production of a part using the process entails dipping a workpiece in a dielectric fluid, clamping it in a machinist vise and then making the wire run through it to create sparks during the flow of an electric current.
How EDM Cut Wire Technology Works
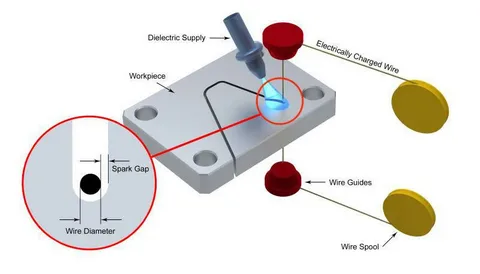
The EDM cut wire method works by the concept of regulated electrical discharge among two electrodes at a spark gap . Wire EDM process involves an electrical spark between the two conductive components, a wire that is followed and a component in which the material needs to be taken. No physical contact is made with the working piece, instead there is an accurately spaced gap between the wire electrode and the working piece and it is this gap that limits incoming energy and as such provides very tight cutting with no mechanical influence or distortion.
The Science Behind Electrical Discharge Machining
Electrical discharge machining (EDM), in some cases referred to as spark machining, spark eroding, die sinking, wire burning or wire erosion is the process of electric discharge machining fabricating metal by controlling electrical discharges (typically sparks). A great level of heat up to 8,000 degrees Celsius to 12,000 degrees Celsius is produced and the work piece material gets melted and vaporised instantly. This very high temperature is specifically controlled, as well as spatially localized, and exerts its effects only on the material at the surface as it does not interfere with the heat processing of the body structure below.
Key Components of EDM Cut Wire Systems
The contemporary cut wire systems in EDM have a series of very important items that are in synchronization with each other to ensure that precise cutting is completed even under tighter tolerances . The cutting tool is a wire electrode which is usually made of brass or stratified copper materials. The electrical pulses produced by power supply around hundreds of thousands of discharges per second are controlled. Deionized water is employed as a dielectric solution in terms of regulating conductivity, and as a coolant and slurry carrier to eliminate the eroded particles. Complex geometries and taper cuts complex shape is available due to CNC controls that provide required four-axis motion.
Wire Electrode Materials and Specifications
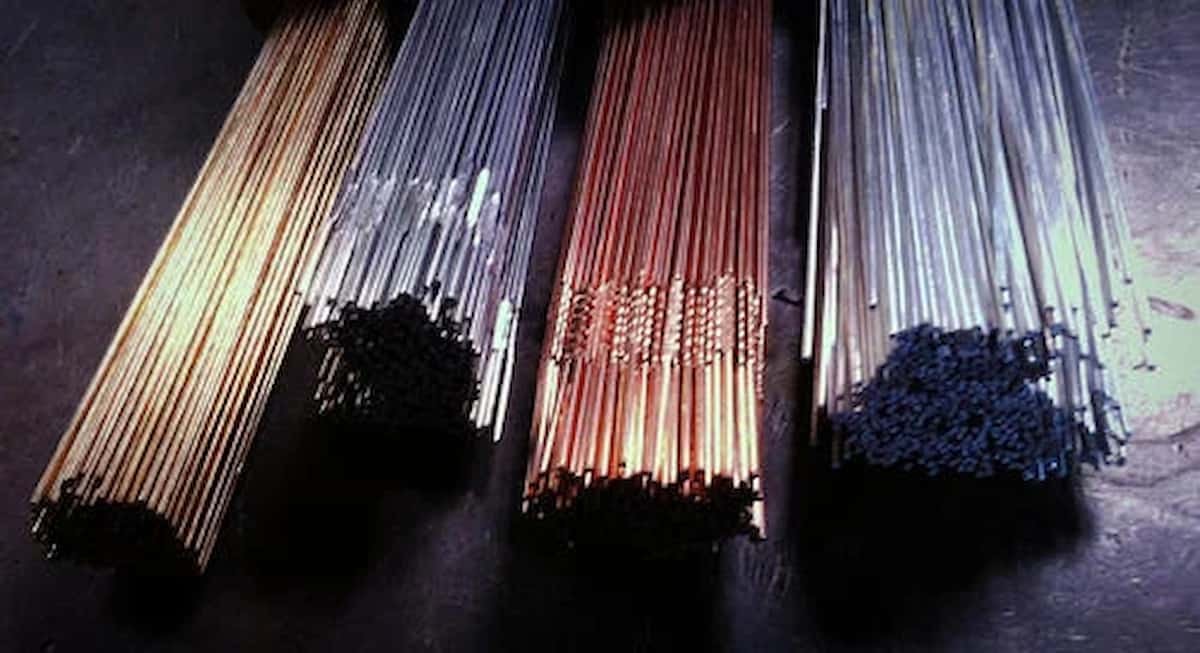

Wire electrode material also plays an important role on cutting performance and quality of the resulting surface finish. Brass wires have very good cutting rates and they can be used in general applications. The precision components have high quality surfaces finish with zinc-coated wires. Copper wires are ideal where optimum conductivity and the rate of cutting is needed. One involves special alloy wires that meet certain material compatibility demand and deliver the best in demanding applications.
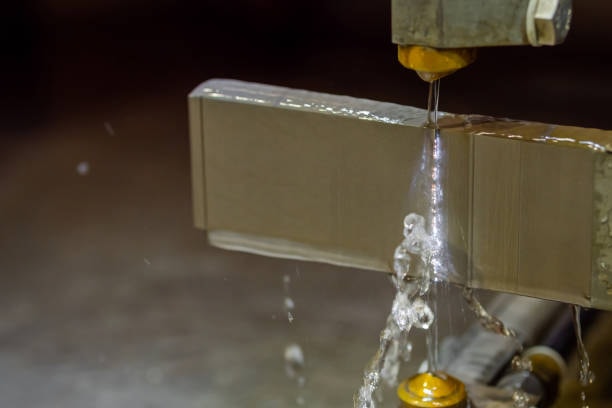
Dielectric Fluid Systems in EDM Cut Wire

The role of dielectric fluid system in operation of EDM cut wire is significant, because it performs many functions at the same time. The dielectric medium mostly used is deionized water whose conductivity level is very carefully maintained to achieve maximum efficiency in electrical discharge process. The fluid is necessary because it cools the work pieces during the high-temperature cutting operation and thus eliminates thermal damage to the product and the wire electrode. Also, microscopic particles produced in the course of the erosion are cleaned up by the dielectric fluid, keeping the cutting conditions clean.
Precision and Accuracy Capabilities
The EDM cut wire technology can offer precise and accurate cuts at the highest levels of precision that are beyond the wire edm process traditional machining processes. The common accuracies attained are between + / -0.0001 and supportive of 0.0005 inches depending on level of geometry of the part and material characteristics. It does not require mechanical forces to cut hence distortion or deflection of materials is avoided as cutting process is uniformly accurate throughout the process. Fine finishes down to 4-8 microinches Ra are normally obtained and there are often no secondary finishing operations.
Material Compatibility and Limitations
A wire electrical discharge machining (a.k.a. wire EDM) is a wire edm machining process, in which an extremely fine (three to five micrometers in diameter), electrically charged wire is used to cut electrically conductive materials with extreme accuracy. The process can accept any conductive electrically material, hard or soft, in whatever heat treatment state. Tool steels, stainless steels, titanium alloys, Inconel, aluminum, brass and copper are common materials. The tormenting and EDM cut wire technology do not process non-conductive materials (or plastics or composites or ceramics), unless there is special coating to allow them to conduct electricity.
Advantages of EDM Cut Wire Technology
EDM cut wire technology has very many benefits as compared to traditional machining techniques. The resultant process is capable of cutting on tough materials that would be hard using conventional cutting tools or even impossible to machine with the conventional methods. Intricate profile, sharp edges and complex internal surface geometry can be easily attained without considering tool wear. There are no mechanical stresses associated with the non-contact cutting, distortion is avoided on fragile or thin walled parts. There is a limited number of heat-affected areas as well as no material properties are lost in the workpiece.
Common Applications in Manufacturing Industries
Cut wire technology used in EDM is more of specialized application in manufacturing. It manufactures turbine blades, engine and structural parts in the aerospace industry that need high tolerances and proper selection of tool electrode . The medical device industry applies the process to surgical equipment, implants, diagnostic equipment components. Applications of tool and die are progressive dies, stamping tools and extrusion dies. EDM cut wire is used in electronics manufacturing as connector components, as a heat sink, and precision enclosures.
Automotive Industry Applications
EDM cut wire is important in the automobile industry when it comes to the production of vital parts in the cars. The engine parts like fuel injection nozzle, valve bodies, and transmissions parts need accuracy that can be achieved only through EDM cutting, minimizing machining time . Wire EDM precision and surface finish requirements Manufacturing of stamping dies of body panels and body structure components is based on wire EDM precision and surface finish capabilities. High flexibility and fast setup time that is provided in EDM cut wire processes are beneficial in prototype development and in small quantity production runs.
Medical Device Manufacturing
The medical equipment manufacturing sector requires the utmost precision and top quality of the surface, and this makes it perfectly impossible without EDM cut wire technology. The surgical equipment must have cutting bevels that are sharp and precise that do not change their geometry during the sterilizing procedure. Orthopedic implants have to have a complex internal geometry and bio compatible surface finish. The dental use is in crown, bridges, and orthodontic appliances that have complex geometries. Essentially, biocompatible materials such as titanium and conductive metals like stainless steel can be machined using the EDM cutting process, which is crucial to the medical fields.
Aerospace and Defense Applications
The use of cut wire technology in aerospace and defense industries makes use of EDM where the industries challenge the implementation of the technology requiring tighter tolerances using challenging applications. Components of the turbine engine have close cooling holes and complicated passages inside which could be restricted with EDM only. The part of the landing gear must be very powerful and with close tolerances. The parts of missiles and rockets have lightweight designs and multi-shaped geometries. Exotic alloys can be machined and high standards of quality can be upheld by cutting using EDM, which thus become a necessity in these industries.
Process Parameters and Optimization
EDM cut wire is a complex process and only with extensive and proper optimization of several parameters of the process, successful operations of a precise machining process are achieved wire edm cutting. The pulse duration influences the removal rates of the materials and the quality of its finish. Cutting speed and rates of wear depend on the level of current peaks. Surfaces and dimensions accuracy is affected by pulse frequency. Feed rates and instances of tension in the wire affect the cutting accuracy and wire tears. The flow rate of dielectrics influences the degree of cooling as well as the effectiveness of debris removal wire edm machines.
Surface Finish and Quality Control
The surface textures formed by EDM cut wire processes are in themselves the property of the process, and they can be made optimal depending on applications. The recast layer is the layer re-solidified material and averaged in thickness 0.0001-0.0005 inches wire edm cutting process. Formation of white layers, which is involved in change of metallurgical structure should be such that it is avoided by close control of parameters. The values of the surface roughness are somewhat dependent on the level of discharge energy and are refinable to rough cutting to mirror finishes by use of multiple skim passes wire edm services.
Cutting Speed and Efficiency Factors
Feed rate of the wire jobs in EDM can vary widely depending upon material, material thickness and the finish required on the surface. Materials that are softer such as aluminum are able to cut faster than hardened tool steels. The thicker parts need a longer cutting time because of harder discharge gaps requirement through stability concerns. Rough cutting jobs have the speeds of material removal at higher rates whereas finish passes focus more on the quality of surface at lower rates rather than speed. Modern systems have automatic optimization of parameters and are achieved to meet speed and quality demands wire diameter.
Tooling and Fixturing Considerations
Successful operations in EDM cut wire requires good tooling and fixturing. The clamping of workpieces has to be strong but not to affect the wire paths and dielectric flow. Datum surfaces have to be properly prepared to guarantee proper positioning of the parts. Softwares of the wire threading system have to support part shape complexity and multiple start holes sinker edm. The materials of fixtures must be non-magnetic dimensionsally stable during the conditions of thermal cycling.
Programming and CNC Control Systems
The advanced EDM cut wire systems are now computer controlled with advanced CNC control to control the control axis movements path to the parts and the parameters of the part. The cutting paths created directly on geometry reduce the time spent programming and minimizes errors by taking the part geometry and creating the necessary cutting paths. Four-axis capability facilitates taper cutting and three dimensional profile wire edm work. The selection of parameters is automatic and the optimal cutting conditions are achieved with regard to specific properties of materials as well as the geometrical needs. The real-time monitoring systems anticipate variations in processes, and they automatically correct them conventional edm.
Quality Assurance and Inspection Methods
Employing strategies of inspection is needed in ensuring quality assurance in EDM cut wire jobs. Coordinate measuring machines and optical measurement systems are used in dimensional accuracy checking. Surface finish measurement uses profilometers and visual techniques of surface finish measurement. Metallurgical testing looks at metals in the recast layer, as well as heat affected-zone properties. Processes of statistical process control watch essential parameters to make a stable quality and detect the process drift machine complex shapes.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
EDM cutting wire operations may be faced by several issues which need methodical trouble-shooting strategy. The most common cause of wire break is using tall cutting parameters and infecting dielectric or wrong attachment wire tension. Poor surface finish can be due to the incorrect parameters set, poor flushing or the wear on the electrodes power supply unit. Thermal effects, mechanical deflection or programming errors may be the cause of this inaccuracy of dimensions. Symptomatic analysis is undertaken systematically to give the corrective action wire breakage.
Recent Technological Advances
The recent development in the EDM cut wire technology has concentrated on high productivity and new abilities. High-frequency power supplies allows faster cut speeds, and improved finishes. Better cooling and debri removal is achieved by advanced dielectric systems electrical components. In adaptive control an optimization algorithm makes automatic adjustments of parameters using feedback in real time. Multi-wire systems allows many parts to be cut together, vastly increasing productivity in high-volume applications.
Industry Standards and Specifications
EDM cutting wire operations should be able to meet a number of industry specifications and requirements. Quality management systems on the basis of ISO 9001 provide consistency and constant progress. AS9100 aerospace standards deal with special needs of the critical applications. Medical device standards such as the ISO 13485 have been developed and regulate the healthcare manufacturing processes small hole edm. Military specifications are requirements that are produced in defense components to meet fantastic conditions and reliability.
Cost Considerations and Economic Analysis
The analyses of EDM cut wire operations economically should not only include initial investment costs in the equipment, but they have to include a variety of promoted costs inherent in the production process fuel system components. Fixed operating costs are costs on wires consumed, power consumption and dielectric maintenance. The costs related to labor differ depending on the levels of automation and requirements of the skills of operators. The non-contact that occurs during cutting is usually a simpler process which makes tooling costs cheaper as compared to the traditional machining. The quality costs can also be optimized in a way that there is better accuracy and less scrapping costs with respect to the traditional systems.
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of EDM cut wire technology can be seen to be so exciting as far as capability and efficiency are concerned. The integration of artificial intelligence will make it possible to predict the maintenance or optimize the parameters automatically. The selection of workpiece and electrode materials will be increased by advanced materials research. Forming a hybrid manufacturing system will integrate EDM into an overall system, which is more flexible. There will be development of more environmentally friendly dielectric systems and energy efficient operations due to impact of the environment.
Conclusion
The EDM cut wire technology remains a revolution in precision manufacturing in a wide variety of industries because they can produce complex geometries and to challenging specifications in unexampled ways. Non-contact cutting process has avoided most of the limitations of conventional machining processes and has offered an excellent level of accuracy and surface finish. With technological development becoming more enhanced in productivity and capabilities as well, it is rather expected that cut wire EDM will persist in serving as a core tool among manufacturers interested in gaining competitive advantages in the production of precision components.

