Learn all the major molding differences and comparison of blow molding to injection molding when you compare blow molding vs injection molding. Find out the prices, supplies, uses and the most suitable method you should choose in relation to your production.
In a decision to select the manufacturing process of plastics, it is important to know the distinctions between the blow molding and injection molding so that people can make sound decisions regarding blow molding and injection. Blow molding can be used to make thin-walled hollow pieces, injection molding resulted in parts with complex shapes and has greater choice in raw materials. This extensive tutorial discusses the two processes in order to enable you to identify the most suitable method of manufacturing that suits your production needs.
What is Blow Molding and How Does It Work?
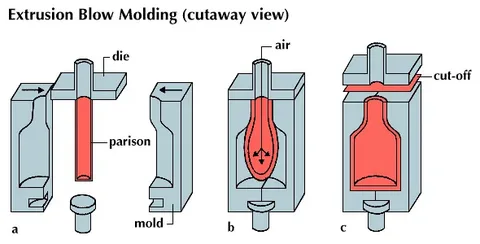
Blow molding is a trade specific type of manufacturing aimed at producing hollow-type plastic items such as a hollow tube of plastic like bottles, fuels tanks, and containers. The mechanism is used to produce hollow products of thermoplastics through preforming followed by subsequent expansion of the product in compressed air to the profile of the mold.
The blow molding is achieved by heating thermoplastic material to rendering its pliable, while hydraulic rams to inject materials ensure precise shaping . The extrusion of a hollow tube known as a parison then follows or injection molded. When this parison isbetween two halves of a mold, which are closed upon it. The parison is filled with compressed air, which makes it stretch with the same shape of the mold inside. After the plastic has cooled and solidified, the mold opens and the complete hollow part is pushed out.
The technique is superior in the making of lightweight low cost hollow containers and components, particularly plastic bottles . It is most applicable to the production of uniform wall thickness products resulting in good internal surface finish and it is therefore applicable towards the packaging and consumer product.
Understanding Injection Molding Process
Injection molding is a flexible process of manufacture whereby hard plastic articles are formed by pushing molten thermoplastic into a closed mold through high pressure. The injection molding process is because an injection molding machine injects molten substance into a dedicated mold and molds products, especially when injection molding compared to other processe . and hence it is applicable to produce complex detailed components with an exact dimension.
The beginning of the process is a portion of the molten plastic substance melted and homogenized in a heated barrel by a rotating screw. When the material is given the desired temperature and consistency, the screw can be operated as a plunger, forcing the molten plastic through a nozzle into the mold cavity at very high pressure, which expands a hollow tube. The mold is clamped using strong hydraulic clamps to ensure the plastic that is high pressure does not get away.
Once the plastic is injected, it is cooled in the mold in integral cooling lines. After the part has solidified into the desired shape, mold are opened and the finished parts are ejected out by the ejector pins. This operation may be repeated and repeated fast, and since injection molding is a smallto- high volume production process it is used best in producing complex plastic parts.
Key Differences Between Blow Molding and Injection Molding
The underlying or rather most basic difference between the two manufacturing procedures is the end products and the application of these products, where blow molding is generally cheaper for hollow design . Blow molded parts are hollow and injection molded part is solid components whereas blow molded parts are not. The difference provides the impetus of several of the other differences between the processes.
Blow molding is run at lower pressures and temperatures than injection molding which influences the equipment needed as well as the kind of material that may successfully be processed. The complexity of the parts which can be made is also dependent on the pressure differences, as in blow molding only relatively simple hollow objects can be created, whereas very complex parts with fine details are possible using injection molding.
The ability of the wall thickness is also substantially different. Blow molding is superior in forming thin walled parts of uniform thickness., whereas injection molding has versatility in the ability to form parts with non uniform thickness and solid cross-sections. This makes every process fit in to different sets of applications and product requirements.
Cost Comparison: Blow Molding vs Injection Molding
Cost utilization of a manufacturing process is a key factor in decisions that surround the manufacturing process selection. Blow molding machinery is usually cheaper than injection molding in comparison with injection mold machinery. and the mold equipment is not as heavy and complicated as injection mold equipment. This means reduced initial capital costs and tooling cost of blow molding.
There is also a difference in the operational cost of both processes. The lower the operating pressures, the lower the blower energy required, and the temperature of the blow molding is lower. The less complicated tooling design implies the quicker setup times, and a minimum of maintenance work. Also blow molding may not need very skilled operator which may save costs on labour.
But the cost calculation becomes more complicated particularly with regard to volumes of production and complexity of parts. Although blow molding is cheaper in terms of startup costs, injection molding may prove cheaper when it comes to high-volume manufacture of complex pieces due to a faster cycle time and production of multiple pieces at a time because many inserts are possible through multi-cavity moulds.
Speed and Production Volume Analysis
Because it is quicker and parts can be done within 60 seconds, injection molding is a process that is suited in large production runs even though tooling costs are more compared to blowing. This difference in speeds has a big effect on production volume and cost of parts at large volumes vacuum forming can produce.
Speed is the benefit of injection molding and it is reached by the speed of material injection and the efficient systems of material cooling. The operation can be over-automated and component parts made, kicked and inspected in endless sequences. In multi-cavity molds, several parts are made simultaneously further adding to the throughput stretch blow molding.
Although slower per cycle, blow molding can make up by running parallel with a number of molds. This is because the blow molding tooling is cheaper; manufacturers can afford to have several sets of mold to run at a time and attain similar volumes of production, compared to injection molding with some applications blow molded products.
Material Compatibility and Selection
The two processes are compatible with a large number of thermoplastic materials, whereas their compatibility and behavior are different. Blow molding is very applicable to such materials as high density polyethylene (HDPE), polyethylene terephthalate (PET) as well as polypropylene (PP) generally cheaper than injection. These materials possess melt strength and flow properties as needed by blow molding manufacturing technologies that form.
Injection molding has a wider range of materials, having a compatibility with thermoplastics excess material, thermosets, thermoplastic elastomers, and even metal-filled polymers. The injection process allows materials with a wide range of flow characteristics and can even work on material that may be difficult to work on in a blow molding process.
The selection of the material influences the process of production besides other properties of the final product, that is, strength, chemical resistance, transparency and cost image credit shutterstock.com pixel. Knowledge of material compatibility plays an important role in the choice of manufacturing process to be adopted in given applications image credit shutterstock.com pixel.
Applications and Industry Use Cases extrusion blow molding
The production volume manufacturing technologies in the packaging industry are dominated by blow molding, especially in bottles, containers, and other hollow plastic products where blow molding is used extensively. Some of the common uses are as bottle bottles, detergent containers, fuel tanks in cars as well as in toys mold from leaking plastic. The process is also deployed in the manufacture of large containers, drums and technical components in which hollow construction gives benefit in weight saving and material savings extrusion blow molding.
As a method of producing fairly complicated solid components, injection molding is applicable across more industries because it is versatile article will compare blow. Sectors of applications are automotive parts, electronic cases, medical equipment, consumer products and industrial parts credit shutterstock.com pixel b. It is specifically useful in the making of such parts that have accurate dimensions mold using compressed air, complicated geometries and incorporated features such as threads, snaps as well as living hinges plastic blow molding components whereas blow molding.
Decisions between processes are usually made based on the demands of the end product in terms of wall thickness, complexity, and quantities, especially when comparing blow molding to injection molding manufacturing process materials used. The knowledge on these areas of applications assists manufacturers in the potential selection of the most suitable process injection blow molding.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Process blow molding process
There are some unique benefits that blow molding presents which are; relatively low tooling costs, top-notch material distribution of hollow products, and making of seamless hollow products. Blow molded containers weigh less, which is of tremendous benefit in using containers in packages, where concerns with the cost of shipping exist molding definition and comparison.
The drawbacks of blow molding are the fact that they can only be used with hollow parts, produce parts that are not very complex, and cannot be used to form parts that require trimming capabilities compared to blow molding injection stretch blow molding. The process also lacks in controlling the thickness of the walls and cannot make much variation in the thickness of the walls of the parts high production volume manufacturing molding compared to blow.
The benefits of injection molding consist of the possibility to manufacture complicated constructions with close tolerances, outstanding surface finish, and the minimum provisions in post-processing heavy duty hydraulic rams. The process is dimensional control and can accommodate more than one multipurpose into one part complex solid components whereas blow molding compared.
The cost of tools however is higher in injection molding, the equipment is also more complex and also the cost of injecting hollow parts can not be efficiently produced plastic into a mold. It is also limited in the production of very thin-walled components and for this reason, material flow and cooling should be considered carefully to prevent defects injection molding forces plastic..
Conclusion
Your specifications and product specifications should also determine which may work best with injection molding and blow molding and which should be done using injection molding. The application of blow molding is favorable in low-cost hollow objects with reduced up-front investment, thus it is quite a suitable choice in pyroprocessing of packaging and containers, whereas injection molding allows for tight tolerances . The injection-molded process allows technical loading and high precision parts and high volume production with better capacity to handle complex moldings, thus this process is applicable in technical applications thin walled hollow parts comparison to injection molding

