Using a CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine’s precision and automation features depends first on turning on it. Whether you are a novice or experienced machinist, correctly running up and initializing your first CNC milling machine guarantees best performance and lowers the possibility of mistakes or breakdowns. Along with tips for guaranteeing a seamless start-up process, troubleshooting techniques, and maintenance advice for long-term efficiency, this guide will walk you through the thorough process of turning on a CNC machine.
Understanding CNC Machines
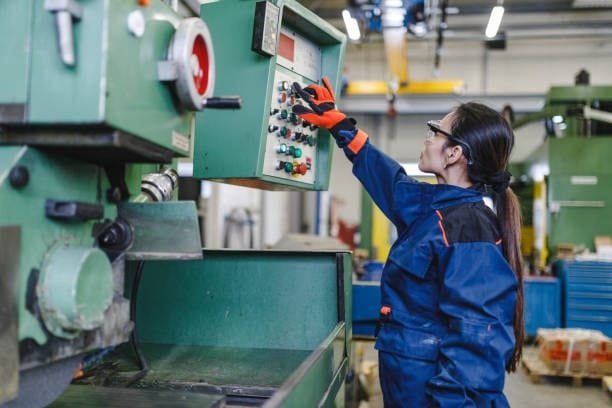

Automated tools under computer control, CNC machines create complex designs with exacting accuracy. They find extensive application in metalworking, woodworking, and manufacturing process sectors. Typical forms of CNC machines consist in:
- Applied for precision cutting, milling, and shaping metal or plastic, CNC Mills
- Designed for rotating the workpiece, CNC Lathes shapes materials.
- Perfect for highly accurate cutting of wood, plastics, and soft metals, CNC routers
- Applied for cutting conductive materials using a plasma torch are CNC Plasma Cutters.
- Using laser beams for exact cutting and engraving, CNC Laser Cutters.
Although every type of CNC machine has a different configuration, most models have a consistent core startup process.
Importance of Proper CNC Start-Up

For several reasons, it is imperative to make sure your CNC and machine tool, is turned on correctly:
- Inappropriate startup could cause tools, workpieces, or machine components to break.
- Starting a machine incorrectly could endanger operators.
- Aligning the axes and calibrating the machine guarantees exact cutting and hence increases accuracy.
- stretches Machine Life: Correct start-up practices and routine maintenance help to lower wear and tear.
Understanding CNC Turning
In subtractive manufacturing, the CNC turning process is the removal of material from a workpiece to attain the intended form. Although cylindrical stock is the most often used form, this technique can also be used on materials in other forms including hexagonal or square bars. While specialized tools precisely cut away material to form the desired shape or design, the CNC machine turns the workpiece.
Types of CNC Turning Machines

Two main configurations for CNC turning machines are vertical and horizontal. Based on the weight and size of the material being machined for different turning operations, every kind horizontal turning center has benefits.
- Perfect for handling big and heavy components, vertical CNC turning machines align the center of gravity of the material along the rotational axis, so guaranteeing stability during the turning operation.
- Usually used for general machining jobs, horizontal CNC turning machines are appropriate for smaller, lighter workpieces.
CNC Turning Axes
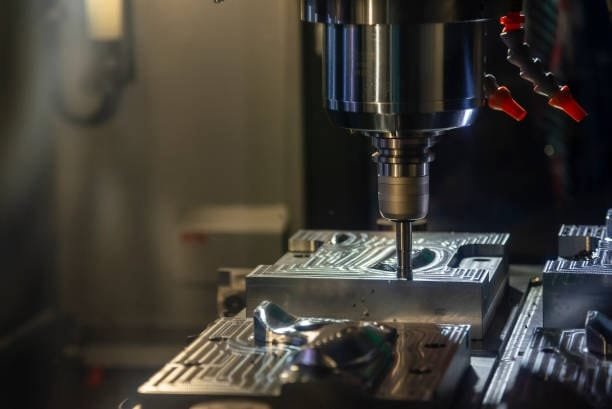

Multiple axes can be found in turning machines; configurations sometimes with multiple cutting tools call for up to six axes. The capacity of the machine to execute difficult cutting operations depends on the number of axes, so enhancing accuracy and adaptability in turning centers in the production process.
Key Components of a CNC Turning Machine
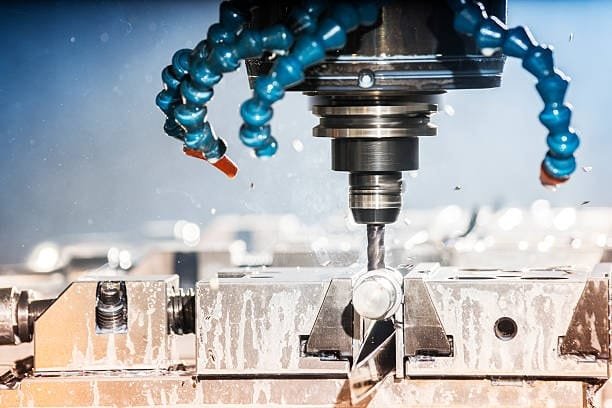

Made of several key parts that cooperate to produce exact machining results, CNC turning machines
- Crucially important to the machine, the spindle holds the chuck on one end and links to the drive system on the other. During the machining process, the chuck controls the workpiece’s securely gripping action.
- Commonly featuring three or four jaws, chuck types While four-jaw chucks are flexible enough to grip square bars or allow off-center turning for specific cuts, three-jaw chucks are the conventional choice for holding round stock.
- Usually CNC turning machines use carbide insert cutting tools. These inserts are rather precise and durable.
- Mounted into tool holders, the carbide inserts are then securely bolted to the turret of the machine. Different cutting tool types call for different specialized holders to guarantee stability. Before machining starts, the turret counts the tools to guarantee flawless and effective operations.
Common CNC Turning Operations
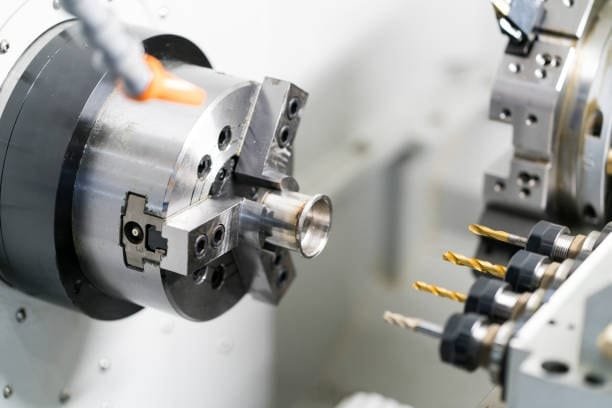
CNC turning machines can shape and polish workpieces by means of several machining operations. The most often used CNC turning tools and techniques in manufacturing industry are listed here:
Facing:
Facing calls for cutting speed by building a flat surface perpendicular to the rotational axis of the lathe machine workpiece. Held in a tool holder on the lathe’s carriage, the cutting tool moves perpendicularly across the rotating part cross slide. This process can be a final pass for a smooth finish or a roughing cut to eliminate extra material.
Turning:
Turning is a process of material removal from cutting edge to the workpiece’s outside diameter. For consistent cuts or a tapered design, it can be done straight turning parallel to the rotational axis or at an angle.
Drilling:
The part’s rotational axis is drilled to produce holes along it. Not limited to the central axis turning involves rotating part, advanced CNC turning centers can drill holes at several orientations.
Boring:
By guiding a cutting a boring tool into the inner wall of a drilled hole, boring widens an existing hole. This technique guarantees exact hole sizes and better surface finish tool life.
Threading:
On a rotating workpiece part, threading either inside or outside helps it to securely screw into other components.
Grooving and Parting:
Cutting small channels into the workpiece to remove material and produce features like O-ring grooves or circlip slots is a cutting process known as grooming cnc lathe machine. Parting separates the completed component from the remaining stock material using a similar instrument.
Knurling:
On a part’s outside, knurling produces a diamond-shaped, textured pattern. The knurling tool compresses the raw material into the proper pattern rather than cutting it. Parts like handles or knobs often have grip added by this process.
Pre-Start Checklist

Use this checklist to make sure your CNC machine is ready and safe before turning on it single point cutting tool:
- Look over the machine for visible damage, loose components, or blockages.
- Make sure the CNC machine is hooked into a consistent power source.
- Check that the emergency stop buttons are not engaged and rather functional.
- Make sure every moving component is lubricated according manufacturer guidelines.
- Check the cutting tools or bits to see they are correctly fastened.
- Check coolant levels if your machine calls for them.
- Verify the workspace is free of obstacles and clean.
- Verify the CNC software load and readiness for the machine to connect.
Step-By-Step Guide to Turning On a CNC Machine
Follow these steps to turn on your CNC machine safely and efficiently:
Step 1: Power Connection
- Before plugging the machine to the power source, make sure the primary power switch is off.
- Make sure there are no loose cables and tightly link the power cord.
- Check voltage needs to guarantee fit with the specifications of your machine.
Step 2: Power On the Main Switch
- To feed the CNC machine with electricity, turn the main switch on. Your machine model will determine whether this requires turning on a dedicated power button or toggling a breaker.
- Verify that the light indicating power flow is turned on.
Step 3: Activate the Control Panel
- Find the CNC control panel then press the assigned power or on button to start the control system.
- During this stage some CNC machines could need you to enter a passcode or start a system reset.
- Make sure the display of the control panel shows normal readings.
Step 4: Home the Machine
- Homing guarantees that every axis of the CNC machine is precisely aligned.
- Finish the homing process according the control panel directions. Precision cutting requires this phase.
- Homing guarantees the machine knows its starting point, so lowering the machining risk.
Step 5: Warm-Up the Machine
- Particularly for highly precise CNC machines, running a warm-up cycle is absolutely vital. This cycle gets the spindle and other moving components ready for seamless running.
- Usually, a warm-up cycle consists in the spindle progressively accelerating to guarantee optimal performance.
- See the manual for your machine for the advised warm-up protocol.
- Make sure no vibrations or unusual noises arise throughout this process.
Step 6: Load the Program
- Load your preferred CNC programme via a linked computer or the control panel.
- Make sure the right file is chosen to stop machining mistakes.
- Verify the program’s directions to guarantee accuracy twice-checked.
Step 7: Run a Test Cycle
- To make sure the machine moves as directed in your program, do a dry run—without material.
- Dry runs confirm spindle speed, tool changes, and cutting paths.
- This stage helps find possible problems before beginning real machining.
- Watch the machine closely throughout this test for indications of misalignment or malfunction.
Troubleshooting Common Start-Up Issues

Think about these options if your CNC machine shows faults during start-up or fails to turn on:
- Check the stability of the power source and guarantee correct cable connections.
- Verify whether the emergency stop is not turned on.
- Review error codes on the control panel and find answers in the manual for your machine.
- Should problems continue, restart the system or reload the CNC program.
- Should the homing process fail, look for sensors or obstructions.
- Examining motor connections will help you to guarantee spindle alignment.
- Environmental Interference: Look for dust accumulation, rust development, or misaligned components should the machine start but fail to run commands.
Safety Tips for Turning On CNC Machines

- Always don the suitable gloves and safety glasses.
- Make sure your desk is clutter-free and tidy.
- When the machine powers on, keep your hands away from moving components vertical turning centers.
- Check emergency stop buttons often for usability.
- In case of an electrical or coolant fire, keep a fire extinguisher close by.
- Use manufacturer recommendations for maintenance and startup practices.
- To reduce risks, teach every employee emergency shutdown techniques.
Maintenance Tips to Improve CNC Performance

Apart from correct start-up, consistent maintenance guarantees optimal operation of your CNC machine:
- Regular cleaning of the machine helps to prevent accumulation of dust, metal shavings, and trash that influences performance.
- Check electrical connections; loose or corroded connections could cause starting problems.
- Check spindle bearings to be lubricated and operating as they should be.
- Regular updates of CNC control software help to guarantee compatibility with new features and safety standards.
- Plan regular inspections in Routine. Professional inspections find possible problems before they affect output.
- Test monthly emergency systems: Make sure kill switches and emergency stops—two safety devices—are completely operational.
Conclusion
Though the turning process on a CNC machine seems simple, following a method guarantees accuracy, efficiency, and safety. Maximizing the performance of your CNC machine requires a pre-start checklist, accurate system power-on, and resolution of any problems. Recall that effective CNC machining process operations depend mostly on tolerance and meticulousness frequently requires continuous supervision. A flexible and exact machining technique, CNC turning helps to produce accurate and complicated components. CNC turning machines can effectively shape materials to fulfill different design criteria using many operations including facing, turning, drilling, boring, threading, grooving, and knurling. Understanding these processes helps producers choose the most appropriate methods to get best results in their production lines.

