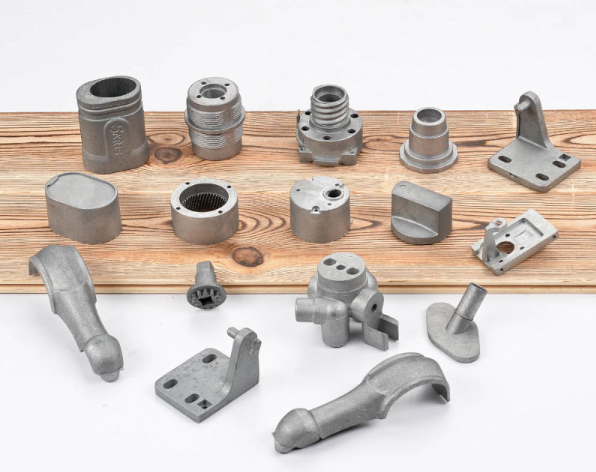
Meta Description: Get to know all about the zinc casting materials, zinc die casting alloys, properties and applications with manufacturing process, including zinc’s low melting temperature . Best practice guide on zinc aluminum alloy, ZAMAK alloys, on ZA series, on auto industry uses and best practices in achieving best castings results in the industry.
The process of zinc die casting technology has transformed the contemporary manufacturing process providing impeccable perfection, durability, and affordability of almost every industry. Zinc die casting materials, considering that it is one of the most versatile and widely used casting processes, offer manufacturers with unmatched opportunities to develop multiple, more complex as well as quality products which attain high performance specification demands, while showcasing various physical and mechanical properties .

Zinc die casting is a very crucial element in global supply chains, which is recognised by GWT Worldwide for its zinc’s excellent bearing properties . With our competencies as a professional logistical engager in worldwide freight forwarding and supply chain solutions we enable ease in transportation of zinc die castings and end products anywhere globally with certain assurance of quality delivery of products and final products by manufacturers to end users/markets in a transnational market, ensuring excellent corrosion resistance .
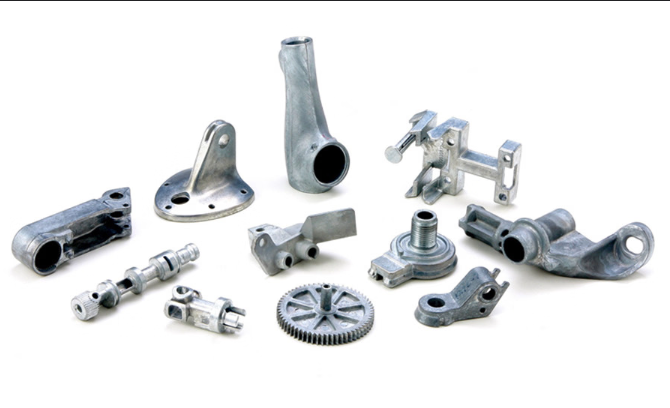
Understanding Zinc Die Casting Fundamental

Zinc die casting is a process of manufacturing in which molten metals (molten zinc) alloy is forced into the highly engineered molds under high injection pressures in steel, utilizing high pressure for better results . The process produces dimensionally precise, complex-shaped parts with the outstanding quality of surface finish and superior strength . Hot chamber die cast zinc alloys possesses zinc’s superior casting fluidity that is extremely excellent and thus such alloy is suitable where complex designs are aimed to be used when thin walls and dimensions tolerances are desired.
The nature of zinc die casting is based on peculiarities of the material, contributing to material cost savings . The low melting point, high fluidity and good casting capability of Zinc allow the manufacturers to make durable components and parts having a tight tolerance such as high precision +/- 0.001 inches and achieve the same quality over longer production cycles.
Primary Zinc Die Casting Alloy Families
ZAMAK Alloy Series

The family of ZAMAK (Zinc- Aluminum- Magnesium- Copper) alloys are the most popularly used material in zinc die casting industrial uses for producing zinc die cast components . The alloys use the inherent characteristics of zinc alloys, with specific properties being improved by the relatively delicate addition of aluminum, magnesium and copper.
The most common zinc alloy used in die casting is zamak 3 due to the castability and the outstanding finishing properties. This alloy gives an ideal compromise and that is why it is used in so many die casting applications, particularly in the automotive industry where high precision and reliable performance compared to other metals is a requirement.
ZA Alloy Series
Overall the ZA alloys are stronger, harder and provide greater creep resistance than the Zn alloys and can be used where bearing properties are critical. ZA (Zinc-Aluminum) ZA-8, ZA-12, and ZA-27 alloys, known as za alloys, all have their unique benefits depending on any particular zinc die casting process applications where mechanical properties of a higher order and wear properties are required.
ZAMAK 3: The Industry Standard

ZAMAK 3 is one of the dominant materials in zinc die cast parts usage partly caused by its unique blend of properties, making die cast zinc suitable for a range of heat sinks and decorative coatings. Its advanced physical and mechanical outstanding properties, good castability and long term dimensional stability, along with the potential for lower production costs, are reasons why many choose it over other materials. This alloy has a content of about 4% of aluminum and 0.035 percent of magnesium that offer good strength to weight ratio and corrosion resistance, contributing to improved die casting production rates .
The elongation characteristics of the alloy allow crimping and swaging processes to be performed and thereby it is suitable in assembly that involve mechanical joining requirements to help reduce fabrication costs . ZAMAK 3 has an outstanding surface finish quality which enables different finishing options to be undertaken, such as plating, painting and powder coating without a rigorous surface preparation work, especially in shot chamber applications .
ZAMAK 5: Enhanced Strength Properties
The enhanced tensile strength as well as hardness of ZAMAK 5 is achieved by increasing the copper percentage as compared to ZAMAK 3, making it suitable for various applications in the zinc die casting process . The alloy offers about 10 percent greater strength and can be cast under high pressure with high rates of castability and dimensional stability. The improved mechanical characteristics result in the ability of ZAMAK 5 to be used for producing zinc parts under the heavier loads compared to its predecessors, surpassing performance of other casting processes .
The increased creep resistance of the alloy increases the service life of the zinc die cast components used in operations where constant loading is used. The machinability of zinc fabricated components like ZAMAK 5 is good, and with its superior creep resistance, secondary operations may be performed where necessary although the as-cast surface finish is so good in most applications no machining is necessary.
Advanced ZA-8 Alloy Properties
ZA-8 alloy has a much-improved strength and hardness level compared with the zinc alloy die casting traditional ZAMAK alloys because it has a lot of aluminium content about 8.4 per cent, providing excellent wear properties . The alloy has tensile strength of more than 290 MPa and good casting capabilities with high dimensional stability.
The higher the quantity of aluminum, the higher the strength-to-weight ratio of the alloy, something which makes the alloy appealing in areas where saving weight is paramount, such as in aircraft. The high level of bearing AB-8 and wear resistance qualifies it to be used in the mechanical fluid areas that experience sliding contact and have cyclic loading, contributing positively to die life .
High-Performance ZA-12 Characteristics
A wonderful bearing alloy, zinc ZA-12 can be plated as well, though the adhesion of the plating is less than what it is in the traditional alloys zinc. It is very powerful alloy with reported yield strength of 380 MPa (55ksi). Its proprietary strength characteristics are among the strongest available with design engineers capable of building lighter, more efficient electrical components with no loss of performance.
ZA-12 is an outstanding bearing material appropriate in bushings, gears as well as other parts that demand high wear resistance. Dimensional stability of the alloy enables the alloy to perform over long durations with little maintenance making the system more reliable.
ZA-27: Maximum Strength Applications
ZA-27 is the strongest alloy of zinc die casting alloy available with about 27 percent of the aluminum content. The alloy offers tensile strengths of more than 420 MPa but having very high properties of hardness and wear resistance. The two-phase microstructure due to the high content of Al, increases mechanical properties drastically.
The combination strength-to-weight ratio of the alloy comes close to that of the aluminum alloys, and retains zincs excellent casting properties. ZA-27 has excellent machinability enabling precision operations to be performed after the secondary casting operation where necessary but in most cases it does not necessitate any machinability due to the high as-casted dimensions of the material.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Zinc die castings compared to other alloys are stronger, tougher, stronger, perform better and offer die casting production rates that lead to economically manufacture cast parts and cost-effective efficiencies. The die casting property of the zinc alloy usually surpasses the property of other alloys like the aluminum alloy, magnesium alloy/ bronze, other plastics and other cast irons.
Knowledge of the mechanical characteristics of the various zinc-alloys, therefore facilitates the best selection of a material to suit a particular job. Zenithal tensile strength of alloy grades is 260 mp (ZAMAK 3) and above 420 mp (ZA-27) respectively and the yield strength is 200 mp (ZAMAK 3) and 380 mp (ZA-27).
Surface Finish and Dimensional Accuracy
The alloy die cast zinc offers ductility and strength of impact, thin walls and good surface finish thus preparation of plating and painting is accessible for zinc die cast parts . The high quality of surface finish that zinc die casting can produce, usually obviates secondary finishing processes and so lowers production costs and lead times.
Dimensional accuracy Zinc die casting is capable of dimensional accuracy of +/- 0.002 inches on most dimensions and +/- 0.001 inches when necessary. This accuracy relieves expensive secondary machines procedures and guarantees a constant part quality through huge manufacturing runs.
Automotive Industry Applications
Typical uses consist of: Automotive parts: Some car engines, transmission and other under the hood components take advantage of zinc die casting durability and accuracy. The automotive sector can be described as the biggest user of the zinc die casting alloy as it uses these casts in many important parts.
A high strength zinc-to-weight ratio, resistance to corrosion, dimensional precision, and other factors make zinc fit well in the making of engine parts. Other parts such as intake manifolds, valve covers, thermostat housings, heat sinks and other brackets are ideal candidates where zinc die casting can be used as they require very complex geometries that are only possible to achieve using a zinc (DC).
Engine Components and Powertrain Applications
Zinc has turned out to be one of the popular metals in the automotive parts industry most particularly on such products as door lock housing, pawls and retractor gears and pulleys in the seat belt systems not to mention the camshaft and sensor parts. Complex internal passages and the modification of an intricate geometry in the current engines design is possible due to the exceptional castability of zinc casting material.
Zinc die cast engine parts are carburetor bodies, fuel injection housings, timing chain guides and mounting brackets. The dimensional stability of the material used means that the material operates consistently over engine operating ranges and at the same time maintains clearances that are very much precise to achieve excellent performance.
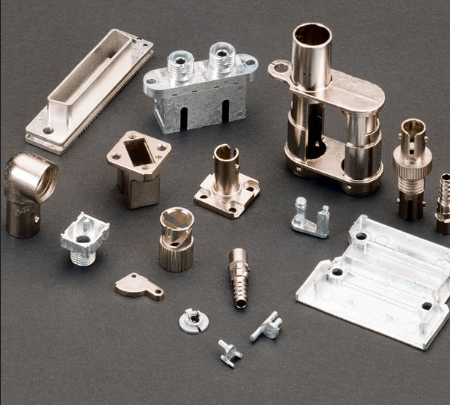
Electronics Industry Applications
Consumer Electronics: The zinc die casting process is employed in producing zinc components, houses and parts of electronic equipment, which guarantees… The energy regulators, switches, ceramic resistors and the wall clocks are produced using the zinc die castings. The environmentally friendly nature of zinc die casting leads the electronics sector to appreciate its use due to their electromagnetic shielding and ability to control dimensions.
Zinc die casting plays an important role in electronics industry where connectors, housings and other components get manufactured. The procedure has great electromagnetic shielding capacities, which protect sensitive electronic devices. Electrical conductivity and shielding effect of material prevent electromagnetic interference of sensitive electronics.
Manufacturing Process Advantages
Zinc diecast needs quite minimal machining. The zinc die-cast features are of very high bearing. Zinc diecast can give you good and accurate dimensional accuracy. This casting technique has a high rate of production compared to any other metal.
Hot chamber die casting which involves zinc alloys will naturally have a greatly increased manufacturing benefit compared to cold chamber methods necessary to cast aluminum and magnesium. Cycles times in the hot chamber process are normally half the time of cold chamber operations making them able to increase production and the per piece price.
Quality Control and Testing Methods
The zinc die casting quality control consists of various testing techniques which guarantee component reliability and performance. Dimensional inspection entails the use of coordinate measuring machines (CMM) used to check the critical dimensions and geometric tolerances. Mechanical property testing also comprises tensile test, yield test, and elongation test of alloy specification.
Internal porosity and the integrity of structure are identified in non-destructive testing methods like X-ray inspection. The use of surface finish ensures the requirements of adhesions using coatings are achieved. The application of the statistical process control ensures that significant variables are observed during the production ensuring the uniformity of the quality level.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Zinc die casting materials are extraordinarily environmentally friendly because they can be recycled and energy saving. Century per cent of zinc alloys can be recycled without the depletion of properties in line with the principles of zinc die casting a circular economy. The low melting point of the material, combined with zinc’s superior casting fluidity, also saves energy on melting and casting exercise than other alloys.
Secondary zinc manufacture using recyclable materials consumes only 23 per cent of the amount of energy required to refine primary zinc. Such energy efficiency together with the natural corrosion resistance offered by zinc that increases service life of the components amounts to sustainable solutions to low-environmental-footprint manufacturing.
Cost Analysis and Economic Benefits
The process of zinc die casting and other casting processes has outstanding economic value because it allows to economically manufacture cast parts and reduces various costs in a number of ways. The high-speed hot chamber operation allows high production rates that lowers labor cost per piece. Easy processing eliminates secondary processing and related cost of tooling.
Surface finish quality with the material used is very good leading to the reduction in finishing operations needed and dimensional accuracy leads to avoiding the cost of adjusting assembly. Tooling costs are spread over long production runs of high volume creating a advantageous economics to long tool life tooling, which can be in excess of 1 million cycles.
Design Considerations and Guidelines
The best die casting design of zinc takes into consideration certain particular guidelines that make the use of the material to the maximum with minimum difficulty in manufacturing aspects. The wall thickness usually falls between 0.6mm to 6mm and the thickness is duly distributed so that there cannot be any porosity and all the properties of the material can be had consistently.
The angle at the draft is 0.5-1 degree and helps to exert the part and strain the tool as little as possible. A minimum fillet radius of 0.5mm is used to remove stress concentration and to extend tool life. The location of parting line takes into consideration the aesthetic requirements and reduces finishing operations.
Future Trends and Innovations
Technology of zinc die casting still under development by providing new alloys and developing new processes compared to other casting processes . Nano-additions of new alloy compositions increase superior mechanical properties and still exhibit good castability. The vacuum die casting processes eradicate porosity so that they can be applied pressure tight.
There is reduced chance on labor cost with consistency improved through automation. Sensor information provided through IoT can be used to monitor processes in real-time and predictive maintenance as well as optimize quality. Optimization of tooling investment is made possible through simulation software advances to design complex parts.
Industry Standards and Specifications
Die cast materials Zinc materials used in die casting meet many international standards that guarantee consistency in the quality and performance of the products. ASTM B86 designates alloy compositions and mechanical properties to be used in North America. ISO 12844 contains international standards of zinc alloy castings such as that include dimensions tolerances and surface finish norms.
Automobile Industry Requirements SAE J468 sets out requirements of zinc die castings used in automotive industry in terms of mechanical properties, corrosion resistance and testings. These standards provide reliability of components as well as their interchangeability within global supply chains.
Global Market Dynamics
In 2025, Asia-Pacific occupies the most significant proportion in Automotive Parts Zinc Die Casting Market. Demand in the global market of zinc die casting is in a persistent increase induced by automotive electrification, miniaturization of electronic devices and growth in industrial automation.
Factors that have contributed to market growth are: lightweight design, demands, precision manufacturing, and cost reduction. New uses of renewable energy, medical and aerospace devices that require advanced wear properties produce new opportunities in zinc die casting materials.
Supply Chain Management
Management of zinc die casting supply chain entails awareness of availability rates, quality assurance of raw materials and logistics. Preliminary zinc production is also focused on geographical areas that result in supply chain dependencies that must be understood.
We provide end-to-end logistic solutions like air freight, sea freight and China Europe railway logistics in GWT Worldwide that can guarantee quality supply chains of zinc alloys die casting materials aluminum die casting. Our customs clearance, and warehousing facilities are able to support our Just in Time delivery service and our Amazon FBA shipping provides worldwide distribution of completed parts die cast toys.
Quality Assurance Protocols
Quality assurance in zinc die casting involves inspection of incoming materials, process monitoring and testing of finished components. Raw material checking involves examination of chemical composition, grain structure and testing of mechanical properties in order to ensure a product fits into specifications of alloys.
In-process controls monitor the temperature regulation, pressure schedule and cycle consistency allowing favorable casting conditions. The last step of inspection involves verification of dimensions, testing of surface finishes, and verification of mechanical qualities to satisfy needs of customers automotive components.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Challenges that usually exist in common zinc die casting problems would be porosity, cold shuts, and dimensional variations. Poorly done venting, high moisture or low vacuum normally leads to porosity. Measures taken are modifying the vents, drying the materials and the optimization of the vacuum system.
Cold shuts are the condition where the metal flow fronts do not fuse in an effective manner exposing a weak spot. Prevention includes the optimization of the gate layout, heating of the metal and enhanced mold preheating. Dimensional changes frequently arise because of process parameters that are inconsistent necessitating the use of the statistical process control.
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
Globally, the new methods of zinc die casting are in the developmental form and can be classified as same as squeeze casting, semi-solid processing, and integration of additive manufacturing. Squeeze casting unites the quickness of die casting and the pressure of forging producing extraordinary mechanical characteristics. Porosity is minimized due to semi-solid processing that allows complex geometry.
Additive manufacturing allows the fast prototyping of tools and intricate cooling channel design that optimises cycle efficiency and quality of the part. The new techniques allow the utilization of zinc die casting in new ways to achieve greater performances.
Conclusion
The zinc die casting materials are one of the pillars of contemporary manufacturing practice, providing outstanding strength, accuracy, and cost-efficiency interceded, including the ability to create thin wall designs . Ranging the ZAMAK alloys, which offer a high level of consistent everyday use, to the high-performance alloys of the ZA series, which present the highest multi-directional strength and toughness, the variety of zinc die casting alloys present design opportunities in the automotive, electronics, and industrial industries.
The fact that alloy constitution and manufacturing methods as well as quality control continue to improve means that zinc die casting continues to compete favorably with other possible materials and also offers a few special benefits in certain uses. Knowledge of properties of materials, manufacturing capability, and design suggestions allow engineers to maximize component performance with minimum expenses, which helps to reduce fabrication costs .

